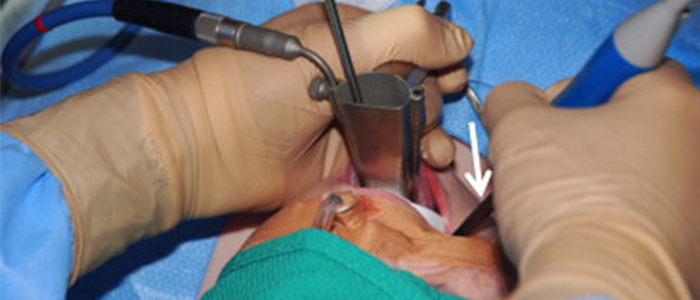
Throat Surgeries
Adenotonsillectomy with Coblater
1) An adenotonsillectomy with coblation is a surgical procedure that removes the adenoids and tonsils using low-temperature radio frequency energy.
2) This technique is less painful and has a lower risk of bleeding than traditional tonsillectomy.